About Human Itch Mites
About Human Itch Mites
There are a lot of mites out there, with scientists having identified over forty thousand unique species. Some of these species are fairly harmless, like the clover mite. Yet others can cause a whirlwind of trouble. The human itch mite is perhaps one of the worst mites that can infect your home, as they spread diseases and can lead to a lot of discomfort.
Appearance
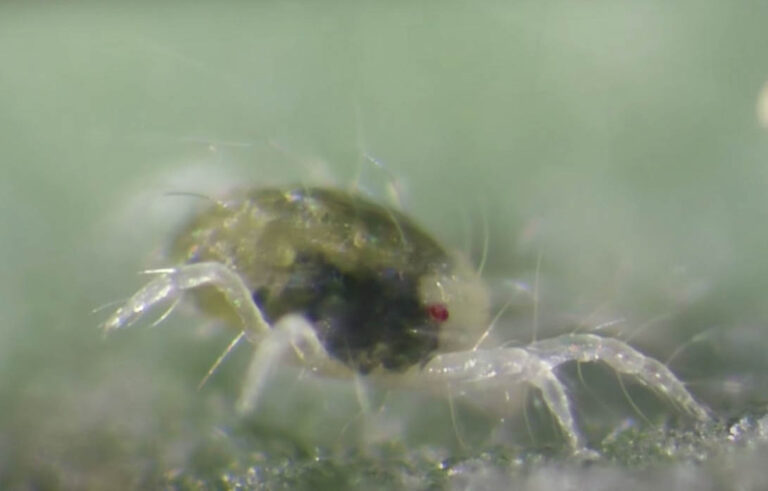
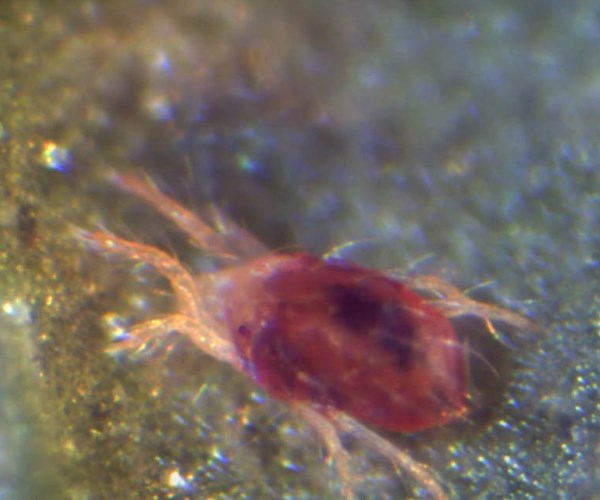
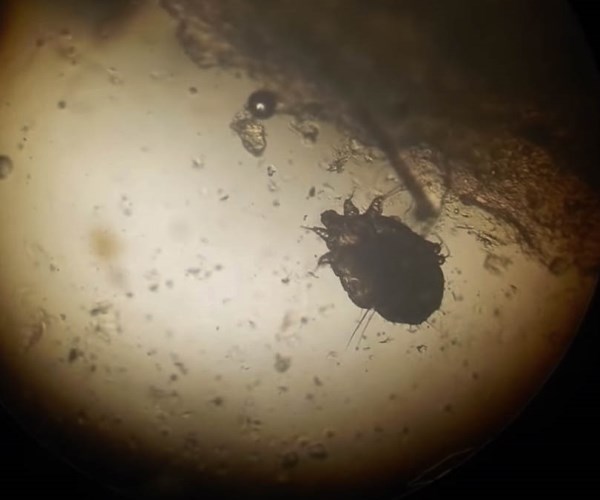
Human itch mites are very small, much like all the other mites they’re related to. These pests tend to be under a sixtieth of an inch in size, so it’s almost impossible to see them with the naked eye. The human itch mite is also slightly translucent, making it even harder to spot them. Yet if you do manage to catch one, you’ll notice that it’s brown or amber in color. Mites are also closely related to spiders and mites, so you can notice eight legs protruding out of their bodies.

Behavior
The human itch mite has a few unique behaviors, but these just make them worse pests. These arachnids tend to feed on people’s skin, but they don’t exactly bite you. Instead, they eat your skin cells, as well as any liquids produced by the cell itself. Yet that’s not what makes them so bad. The reason you should be wary of them is scabies.
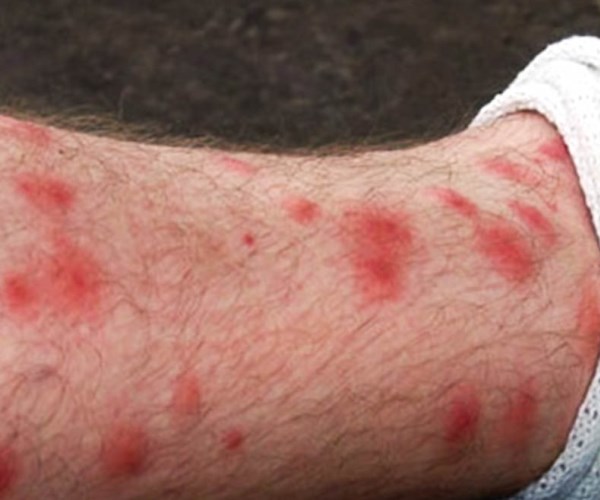
Scabies is a disease that’s only caused by the human itch mite. After becoming fertile, female itch mites will start burrowing under your skin. While under your skin, they start laying their eggs. The eggs then remain under your skin until they hatch, at which point they’ll eventually start burrowing up to your skin’s surface.
It’s all that burrowing that makes scabies so bad, as it leads to severe rashes as your body rejects the mites’ presence. You’ll start seeing bumps and blisters appearing on your skin, often in a straight line. The disease is also followed by a lot of itching, and this only gets worse during the night. Because these mites are so small and so numerous, they can also spread easily. All it takes is to touch someone who’s infected or to put on their clothes.
In addition to scabies, itch mites and their relatives can also infect animals, leading to cases of mange.
Life Cycle
Like many other species of mites, the human itch mite goes through four main stages during its life. These are the egg stage, the larval stage, the nymph stage, and the adult stage.
The egg stage begins under a person’s skin after an adult female mite has burrowed under a person’s skin and laid its eggs. These eggs are invisible to the human eye, as they’re two hundred and fifty times smaller than an inch. The mites spend about three or four days as an egg before they hatch and enter the larval stage of life.
The larvae who emerge from the egg only have six legs, unlike the adults who have eight. They climb up to the surface of the skin, where they build cocoon-like pouches for themselves. They spend another three or four days in these pouches before entering the next stage of life.
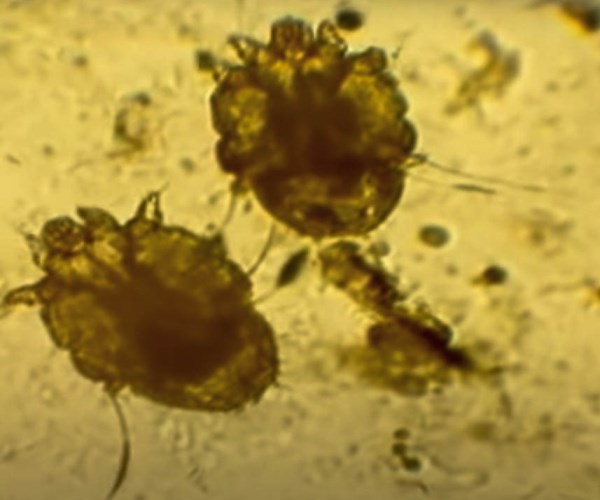
The nymphs are smaller versions of the adults, and they’re unable to reproduce.
They eventually become adults and are able to mate. Human itch mites only mate once per life, as that’s enough to keep the female mite fertile for the rest of her life. She then burrows under a person’s skin and lays about two eggs a day. This goes on for the remaining month or two of her life before she inevitably dies inside the burrow she made.
Habitat
According to the CDC, human itch mites can be found all over the world, where they regularly infect all sorts of people.